Off-Grid vs. On-Grid and Hybrid Solar Energy Systems
Comparisons for making informed decisions:
Solar energy has become an increasingly popular source of renewable energy in recent years, and it's easy to see why. Not only is it a clean and sustainable source of energy, but it also has the potential to significantly reduce electricity bills and carbon emissions. When it comes to solar energy systems, there are two main types: off-grid and on-grid.
Off-grid solar energy systems are designed to operate independently of the electrical grid. These systems typically include solar panels, a battery bank for energy storage, and an inverter to convert the DC energy produced by the solar panels into AC energy that can be used in the home or business.
On-grid solar energy systems, on the other hand, are connected to the electrical grid and operate in conjunction with it. These systems typically include solar panels, an inverter to convert the DC energy produced by the solar panels into AC energy, and a net meter to measure the energy produced and used. Any excess energy produced by the system can be sold back to the grid.
In this blog, we will explore the four main differences between off-grid and on-grid solar energy systems, including cost, reliability, energy storage, and power output. We will introduce the concept of hybrid solar energy systems, which combine features of both off-grid and on-grid systems to provide increased flexibility and reliability. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of the various solar energy options available and be better equipped to make an informed decision when choosing a solar energy system.
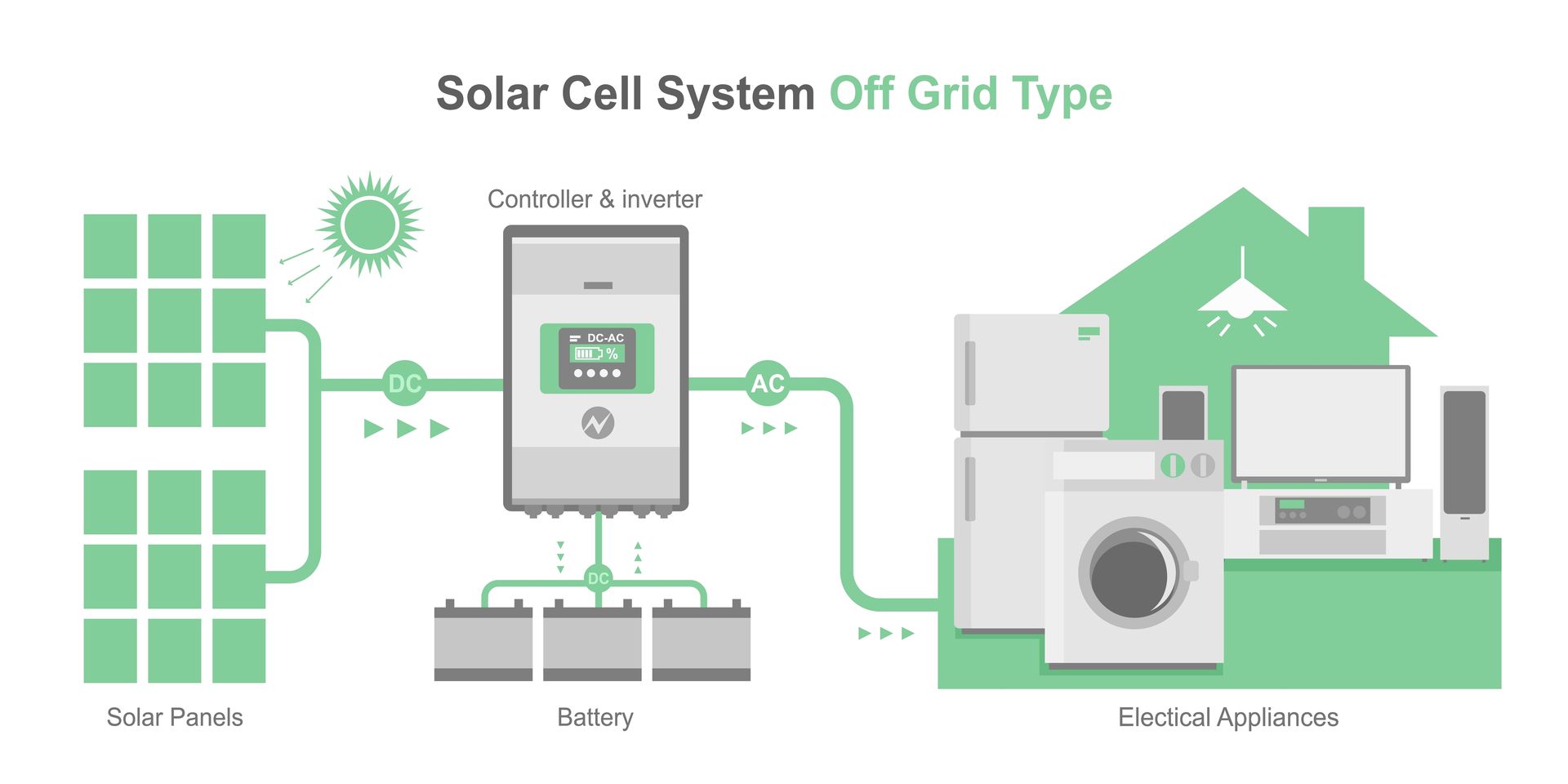
Understanding Off-Grid Solar Energy
Off-grid solar energy refers to a system that is designed to operate independently of the electrical grid. This type of solar energy system typically includes solar panels, a battery bank for energy storage, and an inverter to convert the DC energy produced by the solar panels into AC energy that can be used in the home or business.
The benefit of off-grid solar energy is energy independence. With an off-grid solar system, you are not dependent on the electrical grid for power, which means that you can generate your own electricity and reduce your reliance on fossil fuels. This can be especially beneficial for those living in remote areas where grid electricity is not available.
Another benefit of off-grid solar energy is reduced electricity bills. Since you are generating your own power, you do not have to pay for electricity from the grid. This can be a significant cost savings over time, especially as electricity prices continue to rise.
However, off-grid solar energy systems also come with some challenges. One challenge being the need for backup power. Since solar panels only generate power when the sun is shining, it is important to have a backup power source, such as a generator or wind turbine, to provide power when the sun is not shining. This can add to the overall cost of the system.
Another challenge of off-grid solar energy is the initial cost of installation. Off-grid solar systems require a larger upfront investment than on-grid systems because they include battery storage and backup power sources. However, over time, the cost savings from reduced electricity bills can offset this initial investment.
Off-grid solar energy can be used in a variety of contexts, from rural communities to tiny homes. For example, in rural communities where grid electricity is not available, off-grid solar energy can provide a reliable source of power for homes and businesses. In tiny homes, off-grid solar energy can provide a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to traditional grid electricity.
TAKE AWAY: off-grid solar energy can provide a range of benefits, from energy independence to cost savings. While there are some challenges to consider, off-grid solar energy can be a great option for those looking to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and generate their own electricity.
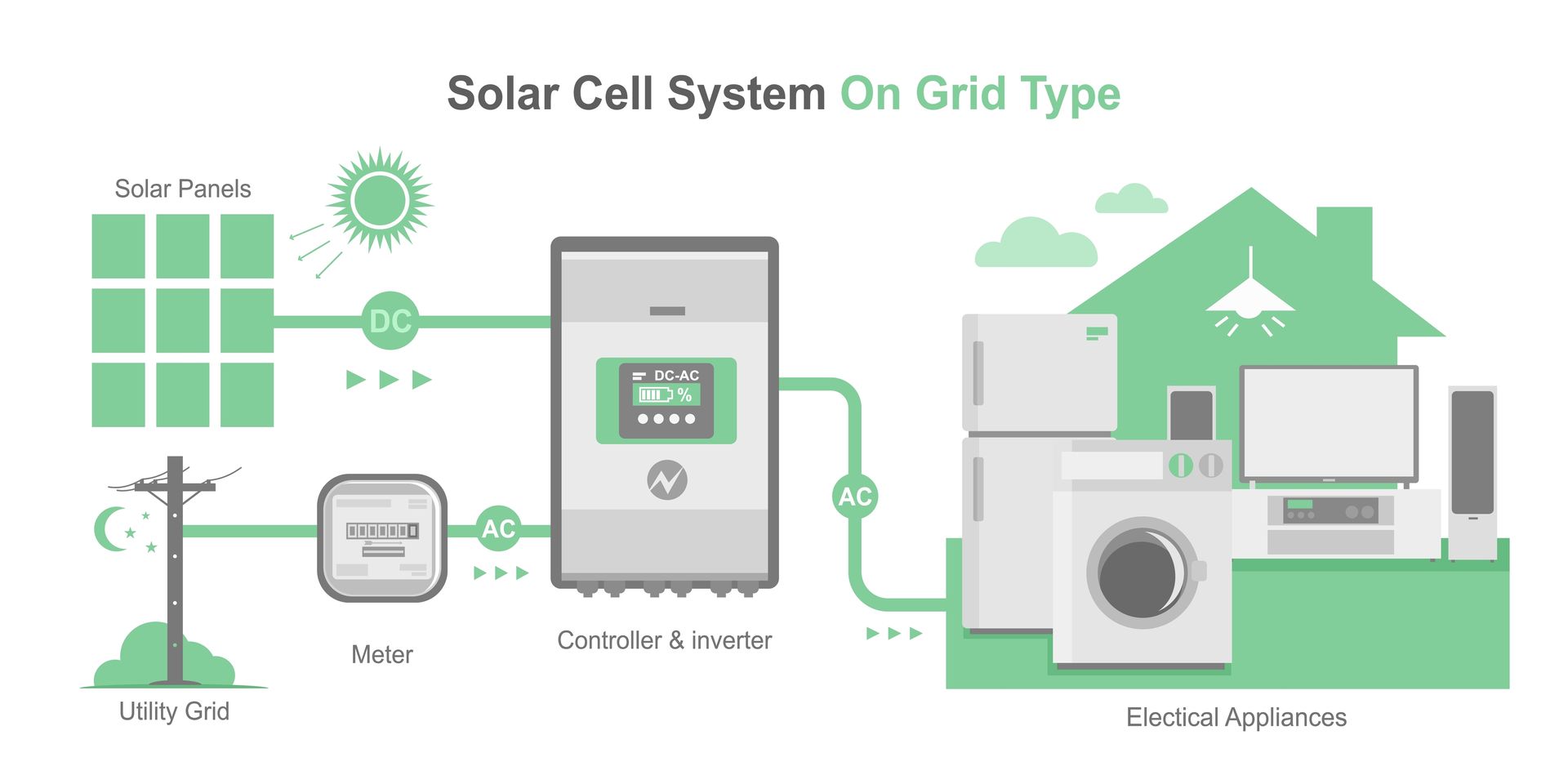
Understanding On-Grid Solar Energy
On-grid solar energy, also known as grid-tied solar energy, refers to a solar energy system that is connected to the electrical grid and operates in conjunction with it. This type of solar energy system typically includes solar panels, an inverter to convert the DC energy produced by the solar panels into AC energy, and a net meter to measure the energy produced and used.
An attractive benefit of on-grid solar energy is lower upfront costs. Since the solar energy system is connected to the electrical grid, there is no need for expensive battery storage or backup power sources. Additionally, many utility companies offer incentives for homeowners or businesses that install on-grid solar energy systems, which can further reduce the cost.
Another benefit of on-grid solar energy is the ability to sell excess power back to the grid. When the solar energy system produces more energy than is needed, the excess energy can be sold back to the utility company for a credit on the electricity bill. This can help offset the cost of electricity during times when the solar panels are not producing enough energy, such as at night or during cloudy weather.
However, on-grid solar energy systems also come with some challenges like the potential for power outages during grid failures. Since the system is connected to the grid, it is still susceptible to power outages if there is a problem with the electrical grid.
On-grid solar energy can be used in a variety of contexts, from residential to commercial buildings. For example, many homeowners are installing on-grid solar energy systems to reduce their electricity bills and their carbon footprint. Similarly, many businesses are installing on-grid solar energy systems to reduce their operating costs and demonstrate their commitment to sustainability.
TAKE AWAY: on-grid solar energy can provide a range of benefits, from lower upfront costs to the ability to sell excess power back to the grid. While there are some challenges to consider, on-grid solar energy can be a great option for those looking to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and take advantage of incentives offered by utility companies.
The Differences Between Off-Grid and On-Grid Solar Energy
In this section, we summarize the differences between off-grid and on-grid solar energy systems and focus on four key differences: cost, reliability, energy storage, and power output. The following table compares and contrasts these differences between off-grid and on-grid solar energy systems:
| Off-Grid Solar Energy | On-Grid Solar Energy | |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Higher Upfront cost due to the need for battery storage and backup power | Lower upfront cost due to no need for battery storage or backup power |
| Reliability | Less reliable due to need for backup power and potential power outages | More reliable due to the connection to the electrical grid |
| Energy Storage | Includes battery storage for energy storage and backup power | No need for battery storage as extra energy can be sold back to the grid |
| Power Outage | Limited during power outage due to the size of solar panels and battery storage | Higher during power outage due to the ability to draw electricity from the grid when needed |
These differences can impact the decision to choose one type of solar energy system over the other. For example, the higher upfront cost of an off-grid solar energy system may be a barrier for some homeowners or businesses, while the potential for power outages with an on-grid system may be a concern for others.
Additionally, the need for battery storage with an off-grid system can impact the amount of energy that can be generated and used. On the other hand, the ability to sell excess energy back to the grid with an on-grid system can provide additional cost savings and make the system more financially feasible.
TAKE AWAY: the decision to choose an off-grid or on-grid solar energy system will depend on individual needs and circumstances. Homeowners and businesses should carefully consider factors such as cost, reliability, energy storage, and power output when making this decision. It may also be worth exploring hybrid solar energy systems, which combine features of both off-grid and on-grid systems to provide increased flexibility and reliability.
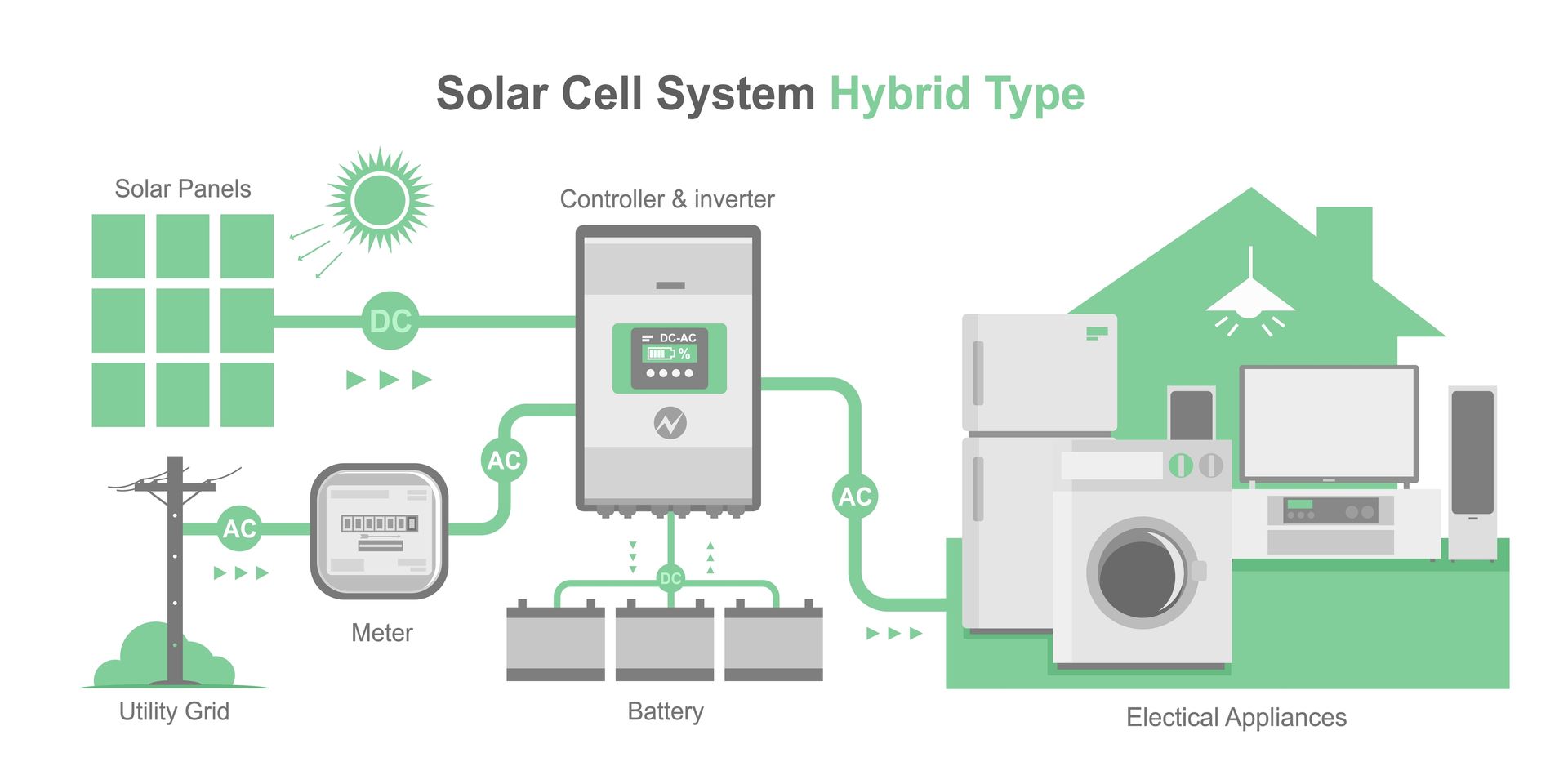
Understanding Hybrid Solar Energy
Hybrid solar energy systems are designed to combine features of both off-grid and on-grid systems. These systems offer increased flexibility and reliability compared to either system alone.
In a hybrid solar energy system, solar panels generate electricity that can be used in the home or business, and excess energy can be stored in battery storage for later use. However, if the battery storage becomes depleted, the system can switch to drawing electricity from the grid to ensure that power is always available.
Increased flexibility is the benefit of a hybrid solar energy system. These systems can be designed to operate as off-grid or on-grid systems, depending on individual needs and circumstances. This can be especially beneficial in areas where grid electricity is unreliable or unavailable.
Another benefit of hybrid solar energy systems is increased reliability. By combining features of both off-grid and on-grid systems, hybrid systems can provide a more stable source of power. This can be especially important for businesses that rely on electricity to operate.
However, hybrid solar energy systems also come with some challenges like the need for more complex installation and maintenance. Since hybrid systems are more complex than either off-grid or on-grid systems alone, they require specialized knowledge and expertise for installation and maintenance.
Hybrid solar energy systems can be used in a variety of contexts, from residential to commercial buildings. For example, in residential buildings, hybrid systems can provide a reliable source of power while also reducing electricity bills. In commercial buildings, hybrid systems can provide a cost-effective alternative to traditional grid electricity, while also demonstrating a commitment to sustainability.
TAKE AWAY: hybrid solar energy systems offer a range of benefits, from increased flexibility to increased reliability. While there are some challenges to consider, hybrid systems can be a great option for those looking to generate their own electricity while also maintaining a connection to the electrical grid.
Conclusion
In this Blog , we have explored the differences between off-grid and on-grid solar energy systems, as well as the benefits and challenges of each. We have introduced hybrid solar energy systems, which combine features of both off-grid and on-grid systems to provide increased flexibility and reliability.
We highlighted four key differences between off-grid and on-grid systems, including cost, reliability, energy storage, and power output. We explained how these differences can impact the decision to choose one type of solar energy system over the other.
Ultimately, the decision to choose an off-grid, on-grid, or hybrid solar energy system will depend on individual needs and circumstances. Factors such as cost, reliability, and energy needs should be carefully considered when making this decision.
Finally, we emphasized the potential for solar energy to play a significant role in reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and combating climate change. As renewable energy technology continues to improve and costs continue to decline, solar energy is becoming an increasingly viable option for homeowners and businesses looking to reduce their carbon footprint and save money on electricity bills.
TAKE AWAY: the adoption of solar energy systems represents a positive step towards a more sustainable future, and we encourage individuals and businesses to consider the benefits of solar energy when making decisions about their energy needs.










