The Future of Renewable Energy: Exploring Solar, Wind, and Hydro Power
Solar Power
Solar power is a form of renewable energy that harnesses the energy from the sun to generate electricity. This is done using solar panels, which convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. This electricity is then converted into alternating current (AC) electricity, which can be used to power homes, businesses, and other facilities.
Solar power has numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced carbon emissions: Solar power produces zero greenhouse gas emissions, helping to reduce the carbon footprint of energy production and combat climate change.
- Lower energy bills: By generating their own electricity, solar panel owners can significantly reduce their monthly energy bills.
- Increased energy independence: Solar power allows individuals and businesses to become more self-sufficient and less reliant on traditional energy sources.
Solar panels work by capturing photons from the sun and converting them into DC electricity. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect. Solar panels are made up of solar cells, which are typically made of silicon. When sunlight hits the solar cells, it knocks electrons loose from their atoms, creating a flow of electricity.
There are several different types of solar panels, including:
- Monocrystalline: These panels are made from a single silicon crystal and are highly efficient.
- Polycrystalline: These panels are made from multiple silicon crystals and are slightly less efficient than monocrystalline panels.
- Thin-film: These panels are made from a thin layer of photovoltaic material and are less efficient than crystalline panels, but can be used in a wider range of applications.
The installation process for solar panels typically involves several steps, including:
- Site assessment: A technician will assess the site where the panels will be installed to determine its suitability and identify any potential obstacles.
- System design: A solar system design will be created that takes into account the energy needs of the facility and the available sunlight.
- Panel installation: The solar panels will be installed on the roof or ground using mounting hardware.
- Inverter installation: An inverter will be installed to convert the DC electricity produced by the panels into AC electricity that can be used by the facility.
- Connection to the grid:
The solar system will be connected to the grid so that excess electricity can be sold back to the utility company.
The costs of installing a solar system vary depending on a variety of factors, including the size of the system and the location of the installation.
There are several incentives available that can help offset the cost of installation, including:
- Federal and provincial tax credits: The federal government and some provincial governments offer tax credits for the installation of solar systems.
- Net metering: Net metering allows solar panel owners to sell excess electricity back to the utility company, reducing their overall energy costs.
- Green Energy Act: Some provinces have implemented green energy legislation that requires utility companies to purchase a certain percentage of their energy from renewable sources, creating a market for solar panel owners to sell their excess electricity.

Wind Power
Wind power is a form of renewable energy that uses the wind to generate electricity. This is done using wind turbines, which convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electricity.
Wind power has numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced carbon emissions: Wind power produces zero greenhouse gas emissions, helping to reduce the carbon footprint of energy production and combat climate change.
- Lower energy bills: By generating their own electricity, wind turbine owners can significantly reduce their monthly energy bills.
- Increased energy independence: Wind power allows individuals and businesses to become more self-sufficient and less reliant on traditional energy sources.
Wind turbines work by capturing the kinetic energy of the wind and converting it into electricity. This is done using blades that rotate when exposed to wind. The rotation of the blades turns a shaft, which is connected to a generator that produces electricity.
There are several different types of wind turbines, including:
- Horizontal-axis: These turbines have blades that rotate around a horizontal axis and are the most common type of wind turbine.
- Vertical-axis: These turbines have blades that rotate around a vertical axis and are less common than horizontal-axis turbines.
- Offshore: These turbines are installed in bodies of water and are typically larger and more powerful than onshore turbines.
The installation process for wind turbines typically involves several steps, including:
- Site assessment: A technician will assess the site where the turbine will be installed to determine its suitability and identify any potential obstacles.
- Turbine selection: A wind turbine will be selected based on the energy needs of the facility and the available wind resources.
- Foundation construction: A foundation will be constructed to support the weight of the turbine and anchor it to the ground.
- Tower installation: The tower will be erected on the foundation, and the turbine will be installed on top of the tower.
- Electrical system installation: An electrical system will be installed to connect the turbine to the facility's electrical system and the grid.
The costs of installing a wind turbine vary depending on a variety of factors, including the size of the turbine and the location of the installation.
There are several incentives available that can help offset the cost of installation, including:
- Federal and provincial tax credits: The federal government and some provincial governments offer tax credits for the installation of wind turbines.
- Feed-in Tariff Program: The Feed-in Tariff Program provides long-term contracts to renewable energy producers, guaranteeing a fixed price for the electricity they produce.
- Ontario MicroFIT Program: The Ontario MicroFIT Program provides a simplified process for individuals and small businesses to connect renewable energy systems to the grid and sell their excess electricity.
It is worth noting that wind power, like solar power, is an intermittent source of energy, as it is dependent on wind availability. Therefore, it is important to have energy storage systems or other forms of backup power to ensure a reliable supply of electricity. Despite this challenge, wind power has significant potential to contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
TAKE AWAY: wind power is a promising renewable energy source that offers numerous benefits, including reduced carbon emissions, lower energy bills, and increased energy independence. With continued innovation and government support, wind power has the potential to play a major role in meeting the growing demand for clean energy.
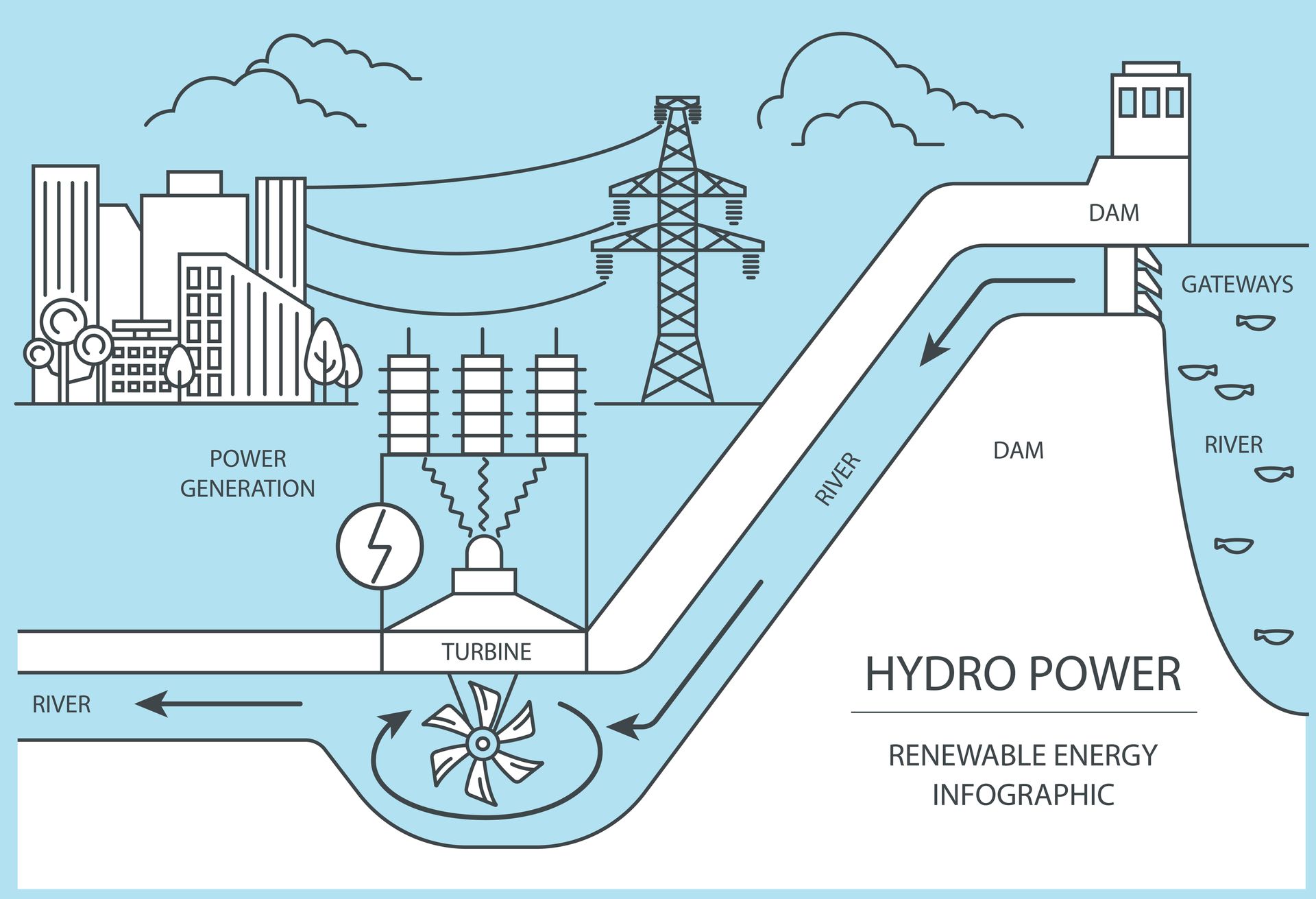
Hydro Power
Hydro power is a form of renewable energy that uses the energy from flowing water to generate electricity. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy, accounting for approximately 16% of global electricity generation.
Hydro power has numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced carbon emissions: Hydro power produces zero greenhouse gas emissions, helping to reduce the carbon footprint of energy production and combat climate change.
- Reliable and consistent energy source: Hydro power is a reliable and consistent source of energy, as it is not dependent on the availability of sunlight or wind.
Hydro power works by using the energy from flowing water to turn a turbine, which is connected to a generator that produces electricity. The amount of electricity produced depends on the flow rate and the height of the water, known as the head.
There are several types of hydroelectric power plants, including:
- Run-of-river: These power plants use the natural flow of a river to generate electricity, without the need for a dam.
- Reservoir: These power plants use a dam to create a reservoir of water, which is used to generate electricity as it flows through a turbine.
- Pumped-storage: These power plants use excess electricity during low-demand periods to pump water from a lower reservoir to a higher reservoir. The water is then released during high-demand periods to generate electricity.
The installation process for a hydroelectric power plant typically involves several steps, including:
- Site assessment: A technician will assess the site where the power plant will be installed to determine its suitability and identify any potential obstacles.
- Design and engineering: A power plant design will be created that takes into account the flow rate and head of the water, as well as the energy needs of the facility.
- Construction: The power plant will be constructed, which may involve building a dam and constructing a turbine and generator.
- Electrical system installation: An electrical system will be installed to connect the power plant to the grid.
The costs of installing a hydroelectric power plant vary depending on a variety of factors, including the size of the plant and the location of the installation.
There are several incentives available that can help offset the cost of installation, including:
- Federal and provincial tax credits: The federal government and some provincial governments offer tax credits for the installation of hydroelectric power plants.
- Feed-in Tariff Program: The Feed-in Tariff Program provides long-term contracts to renewable energy producers, guaranteeing a fixed price for the electricity they produce.
- Ontario Power Authority: The Ontario Power Authority offers a range of incentives for the development of hydroelectric power plants, including grants and loans.
TAKE AWAY: hydro power is a reliable and consistent source of renewable energy that offers numerous benefits, including reduced carbon emissions and energy independence. With continued innovation and government support, hydro power has the potential to play a major role in meeting the growing demand for clean energy.
Advances in technology are driving the future of renewable energy, making it more efficient, affordable, and accessible. For example, new solar panel designs are increasing efficiency and reducing costs, while advancements in wind turbine technology are improving performance in low-wind conditions. Additionally, energy storage technologies such as batteries and hydrogen fuel cells are becoming more efficient and cost-effective, enabling greater use of intermittent renewable energy sources.
Investment and growth in the renewable energy sector are also key factors shaping the future of clean energy. Governments, businesses, and individuals are increasingly recognizing the economic and environmental benefits of renewable energy and investing in its development. According to the International Energy Agency, renewable energy is expected to account for 90% of new power capacity additions by 2025.
The future of renewable energy presents both challenges and opportunities. One challenge is the intermittency of renewable energy sources, which requires energy storage or backup power to ensure a reliable energy supply. Another challenge is the need for infrastructure development to support the growth of renewable energy, such as transmission lines and charging stations for electric vehicles. However, there are also significant opportunities, including job creation, economic growth, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. The transition to renewable energy also presents an opportunity to promote energy equity and access in underserved communities.
TAKE AWAY:, the future of renewable energy is bright, driven by advances in technology, investment and growth in the sector, and the recognition of the economic and environmental benefits of clean energy. However, the transition to renewable energy will require continued innovation, investment, and policy support to overcome challenges and seize opportunities for a more sustainable future.
Hours & Address
Monday --- 9:00 AM–4:30 PM
Tuesday --- 9:00 AM–4:30 PM
Wednesday --- 9:00 AM–4:30 PM
Thursday --- 9:00 AM–4:30 PM
Friday --- 9:00 AM–4:30 PM
Saturday --- by appointment only
Sunday --- by appointment only
12667 Highway 35, Unit 2,
P.O. Box 514,
Minden ON K0M 2K0
Navigation Links
Copyright © 2024 Haliburton Solar and Wind - All Rights Reserved.










